Arterial spin labeling for the measurement of cerebral perfusion and angiography
ASL 作用:quantitative measurement of cerebral perfusion and cerebral angiography ASL 主要类型:PASL (pulsed ASL), CASL (continuous ASL), vsASL (velocity-selective ASL), pCASL (pseudo-continuous ASL)
flow-driven adiabatic inversion
Basic Principles of Arterial Spin Labeling: Continuous versus Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling
问题:
- bSSFP readout
- AIF, residue function
- 为什么要measure perfusion,perfusion是只测量一个很小的区域吗,blood到了这个区域就停止了吗?
- 怎样通过navigator 去correct motion
Physical Principles of ASL
pCASL
a single long pulse is replaced with multiple (up to a thousand) millisecond pulses实现同样的inverse spin的目的
原理类似:off-resonance magnetization profile familiar from steady-state free precession pulse sequences
SSFP: a train of equidistant RF pulses with TR$\ll$T2
可能造成误差的原因:poor shimming
不知道怎么推出来这个Mz
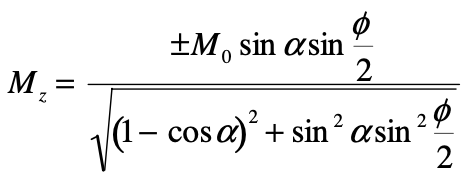
control sequence 中RF pulse怎么改变phase
gradient blips 为什么可以帮助compensate errorneous phase shift
CASL
the blood water is inverted as it flows through the brain in one plane. CASL is characterized by one single long pulse (around 1-3) seconds.
Principle: continuous RF pulse 2~4s + magnetic field gradient in the direction of flow → label thin slice at neck
Disadvantage:
Magnetization Transfer (MT): partial saturation of macromolecules, reduction in the signal from free water in the studied volume
high SAR
PASL
blood water is inverted as it passes through a labeling slab (of 15 to 20 cm) instead of a plane
very short RF pulse over large labeling zones
变形:FAIR, EPISTAR, PICORE, QUIPSS II,
Addition pulse sequence considerations
Readout:
- Multi-slice的问题是post labeling delay对每个slice是不同的,需要考虑进去
- 3D acquisition 没有这个问题,但是coverage 和 resolution会受限
- 通过每次acquisition读出不同region可以获得更大的coverage
ASSIST: 去除静止的背景信号?
Motion correction:
- navigators to estimate
- identify problematic raw data
Advanced labeling scheme
see Advances in arterial spin labelling MRI methods for measuring perfusion and collateral flow
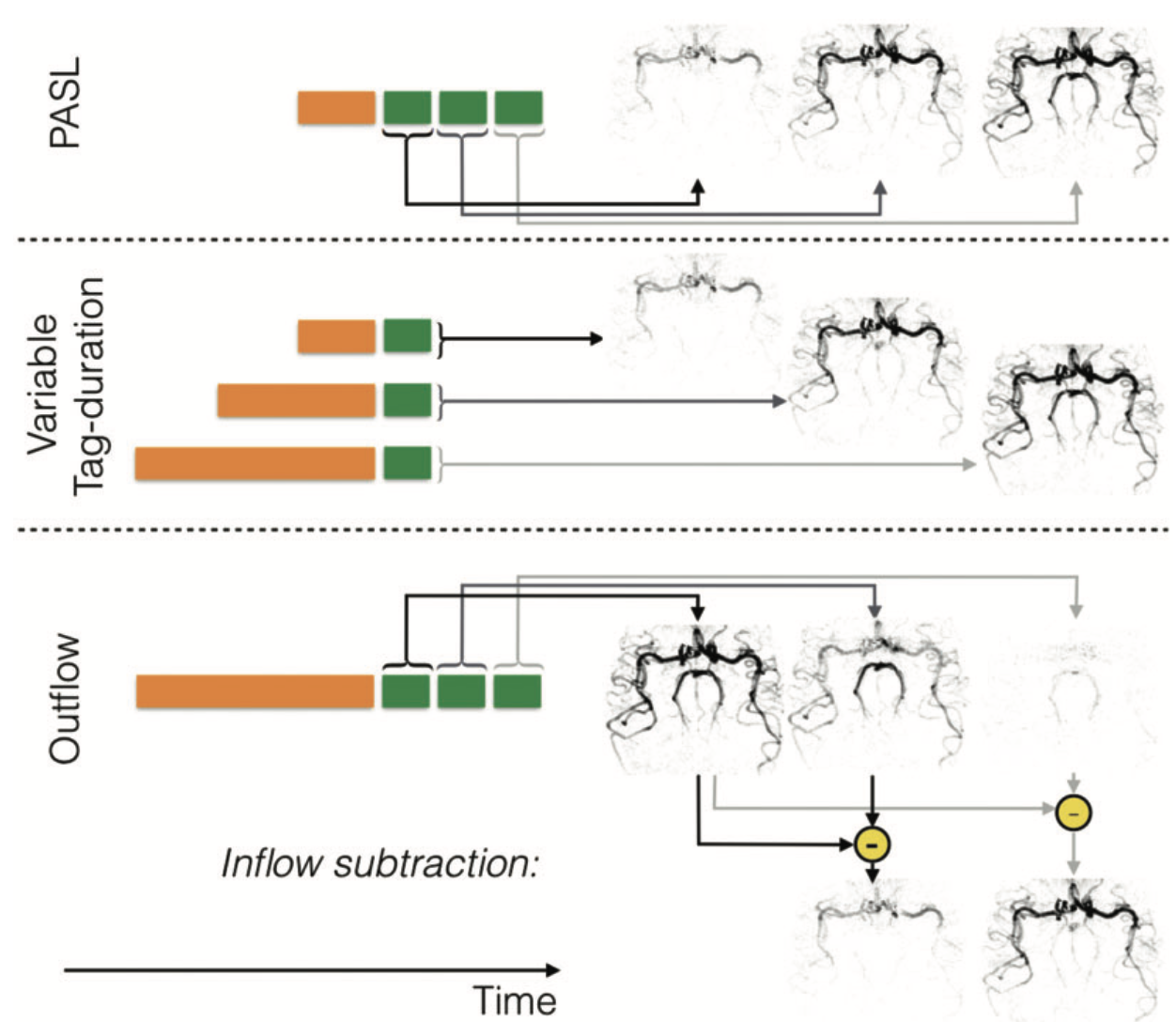
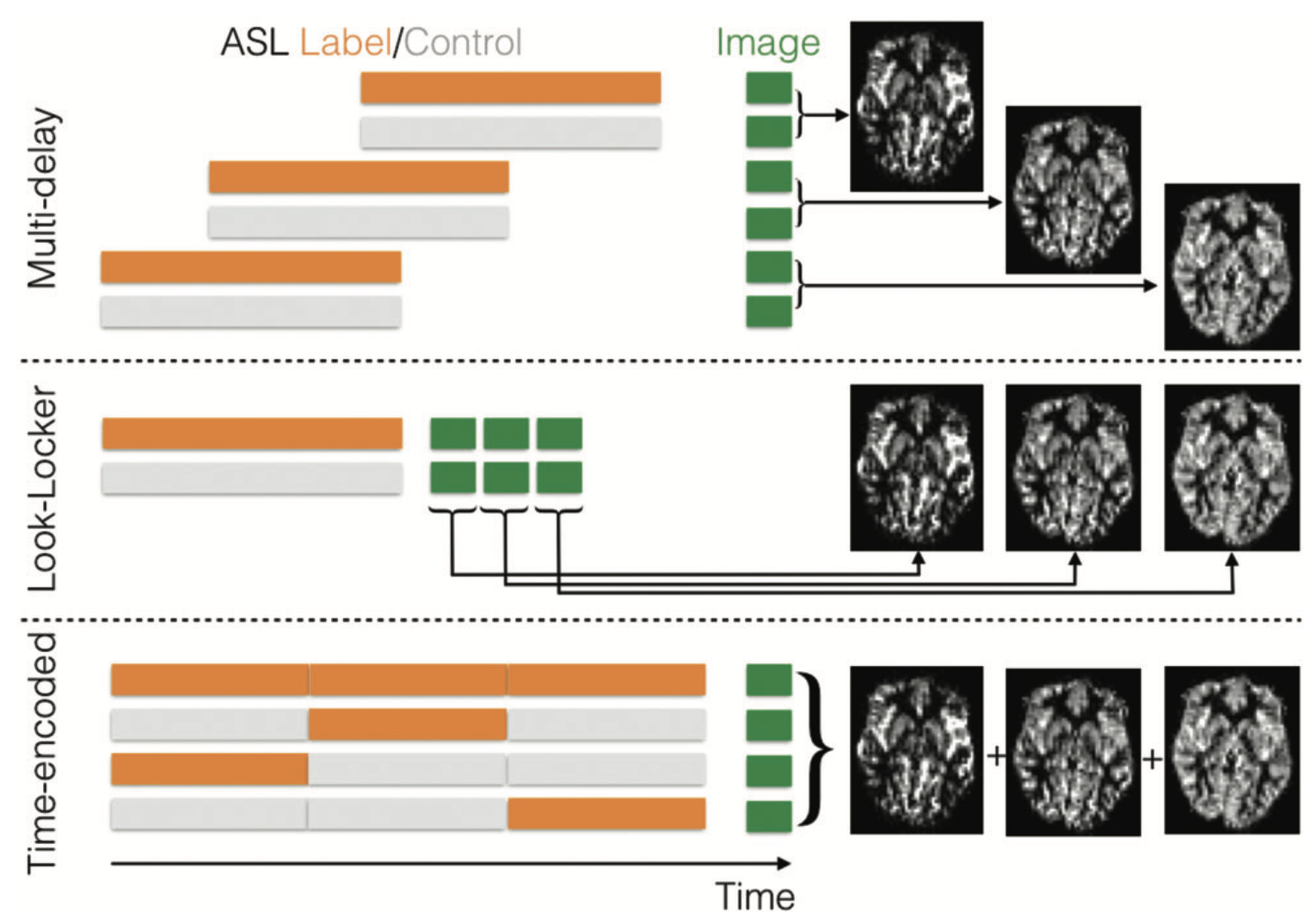
Multi-delay and time-encoded preparations
一般ASL会固定post labeling delay,多次label/control/acquisition,再取平均。这要求在delay time中,所有的labeled blood 在acquisition 就已经到达 imaging plane,同时时间不能太长防止完全relaxation。但是ATT事先并不能知道。
如果想要确定ATT,acquire image at various delays
velocity-selective labeling
- velocity above $v_c$ is labeled
- then velocity above $v_c$ is crushed
- target the spin from above $v_c$ to below $v_c$
Disadvantage:
SNR penalty, diffusion & eddy distortion, only those move along gradient direction can be labeled
not practical
Vessel-selective labeling
motivation:
- 看似正常的perfusion可能实际上是其他artery 的 collateral flow
- incorrect assignment of an infarct to a particular feeding artery
- Single artery selective methods
- limited excitation field
- pencil beam 2D RF pulse, rotate the labeling plane
- modified pCASL, gradient blips between RF pulse, reduction in the size of labeling spot
SNR efficiency is reduced
- Vessel-encoded methods
- Hardamard encoding: preserve SNR efficiency
- random encodings: decrease in SNR efficiency
- Fourier based encoding
Kinetic modeling
-
AIF
-
Residue function
-
The simple model
assumes that all label arriving in the voxel remains there
majority of labeled blood water exchanges rapidly from the blood compartment into tissue
clearance of label directly through the vasculature or via back-exchange from tissue to blood is negligible
-
The standard model
-
Model inversion
-
Model based
Variational Bayesian Inference for a Nonlinear Forward Model
Combined spatial and non-spatial prior for inference on MRI time-series
-
Model free
-
Quantification and calibration
$O^{15}$ PET is the gold standard
Partial volume effects
ASL的分辨率~3mm,因此在一个voxel中可能同时包含GM和WM,由于两者的perfusion value不同,导致混合后的数值有偏差
Spatial PV: Partial volume correction of multiple inversion time arterial spin labeling MRI data
ASL angiography